- Home
- About us
- Courses
-
News
Others
- ما العملات المستقرة؟ وكيف يجري تنظيمها؟
- المركزي الصيني يواصل شراء الذهب للشهر العاشر على التوالي
- أسبوع حاسم للسياسة النقدية العالمية.. "الفيدرالي" يتأهب لأول خفض للفائدة في عهد ترمب
- الأسواق تترقب خفض الفائدة.. ورهانات صعود الأسهم والسندات تتراجع
- الأسهم الأميركية تبلغ قمة جديدة مع توسع توقعات خفض الفائدة
- بعد خفض الفائدة.. باول يوحد صف الفيدرالي وسط عواصف السياسة والاقتصاد
- آمال الأسواق تتعلق بمكالمة ترمب وشي اليوم.. وهذا كل ما تحتاج لمعرفته
- فقاعة الذكاء الاصطناعي محور نقاشات البنوك المركزية باجتماعات صندوق النقد
- الاقتصاد العالمي على صفيح ساخن بسبب رسوم ترمب والذكاء الاصطناعي والديون
- أميركا تصعّد المواجهة التجارية مع الصين قبيل قمة ترمب وشي
- أسهم آسيا تتراجع و"بتكوين" تهبط دون 86 ألف دولار وسط قلق الأسواق
- مخاوف فقاعة الذكاء الاصطناعي تحكم قبضتها على وول ستريت
- "بتكوين" تفقد ثلث قيمتها من ذروتها التاريخية
-
Education
- Currency Pair System in the Forex Market
- Features and Characteristics of the Forex Market
- The Concept of Leverage and Its Sizes
- The Concept of Financial Markets
- What Is Margin and How Does It Work?
- Types of Forex Market Participants & Their Purposes:
- Swap Benefits or Rollover in Trading
- MetaTrader 4 Program Explanation
- Calculating the Point Value and Profit/Loss Calculation
- Types of Trading Orders in Forex
- Forex Trading Mechanism
- Trading Contracts in the Currency Market
- Understanding Price Movement in the Forex Market
- Understanding Forex Market Sessions and the Power of Liquidity Overlaps
- Top 8 Traded Currencies in the Forex Market and Their Global Impact
- Open Live Account
Forex Trading Mechanism
Trading in the forex market is exciting, and one of the main advantages of the currency market is that it allows traders to trade in both directions—whether prices are rising or falling—by buying when prices are going up and selling when prices are going down. This is in contrast to the stock market, where trading typically involves buying stocks at lower prices and profiting by waiting for the price to rise, then selling at higher prices.
Buying:
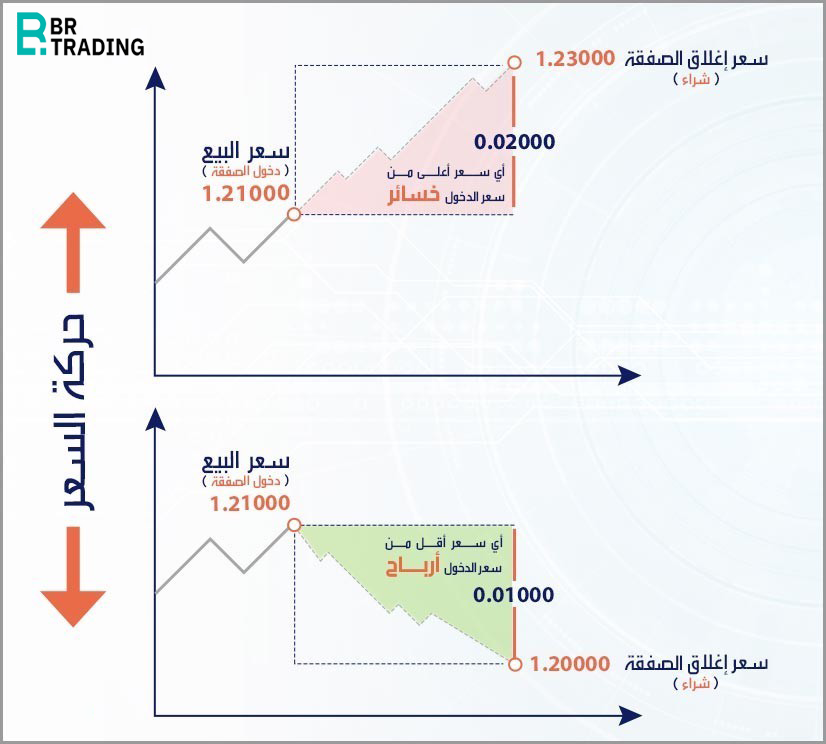
A trader buys a currency pair when they expect the exchange rate of one currency to rise against another. This involves buying the base currency and selling the quote currency. For example: If you expect the EUR/USD exchange rate to rise from 1.2100 to 1.2300, you would buy in order to benefit from the increase. In this case, you would buy the Euro (EUR) and sell the US Dollar (USD). If the price rises as expected, you will make a profit; if it falls, against expectations, you will incur a loss.
Selling:
A trader sells a currency pair when they expect the exchange rate of one currency to drop against another. This involves selling the base currency and buying the quote currency. For example: If you expect the EUR/USD exchange rate to fall from 1.2100 to 1.2000, you would sell in order to benefit from the decline. In this case, you would sell the Euro (EUR) and buy the US Dollar (USD). If the price falls as expected, you will make a profit; if it rises, against expectations, you will incur a loss.
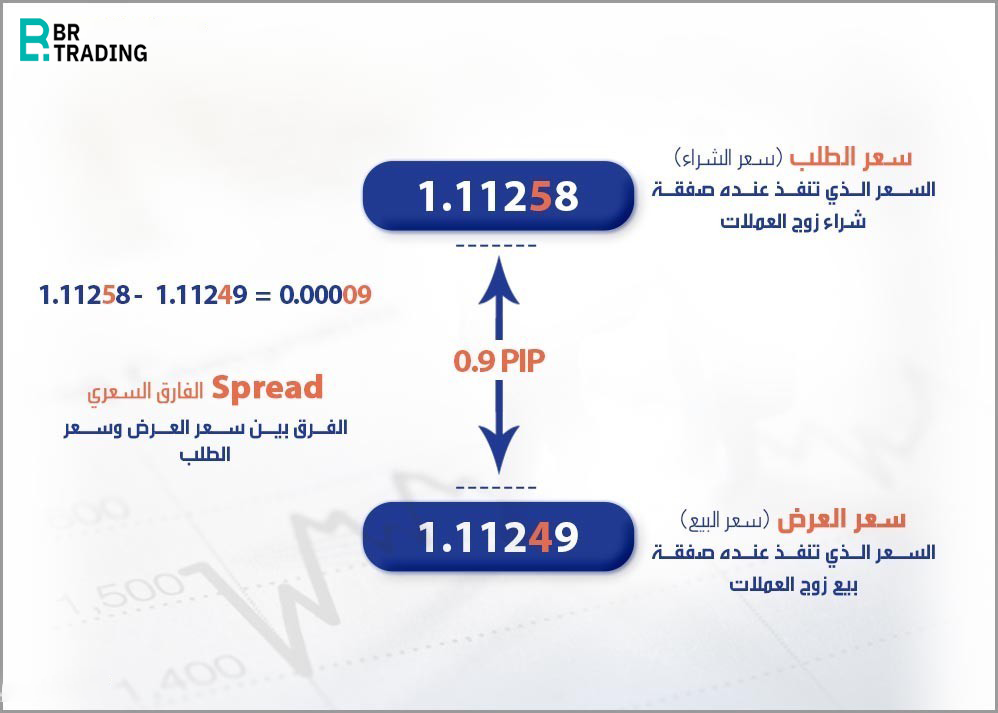
Bid Price and Ask Price
In forex trading, there are always two prices for each currency pair: the bid price and the ask price.
-
Bid Price (Sell Price): This is the price at which the trader can sell a currency pair. It's the price that appears on the trading platform when the trader is selling.
-
Ask Price (Buy Price): This is the price at which the trader can buy a currency pair. It's the price that appears on the trading platform when the trader is buying.

Spread in Forex Trading
The spread is the difference between the bid price (sell price) and the ask price (buy price). The ask price is always slightly higher than the bid price, and this difference is called the spread. The spread is influenced by the available bids and asks in the market. It represents the profit margin for the party executing the trade, whether it's a forex broker, bank, or currency exchange office.
The larger the spread, the more costly the trade will be for the trader. Therefore, the spread is an important factor when selecting a good broker.
The video below explains the concept of the buy and sell prices, as well as the spread and how to interact with the market through them:
How is the Spread Calculated in Forex?
As mentioned earlier, the spread is the difference between the buy price and the sell price. Typically, the spread is determined by the volume of buy and sell orders. The larger the volume of orders for a specific currency pair, the smaller the spread will be, as there is higher liquidity in the market. Traders do not need to manually calculate the spread, as trading platforms automatically calculate it.
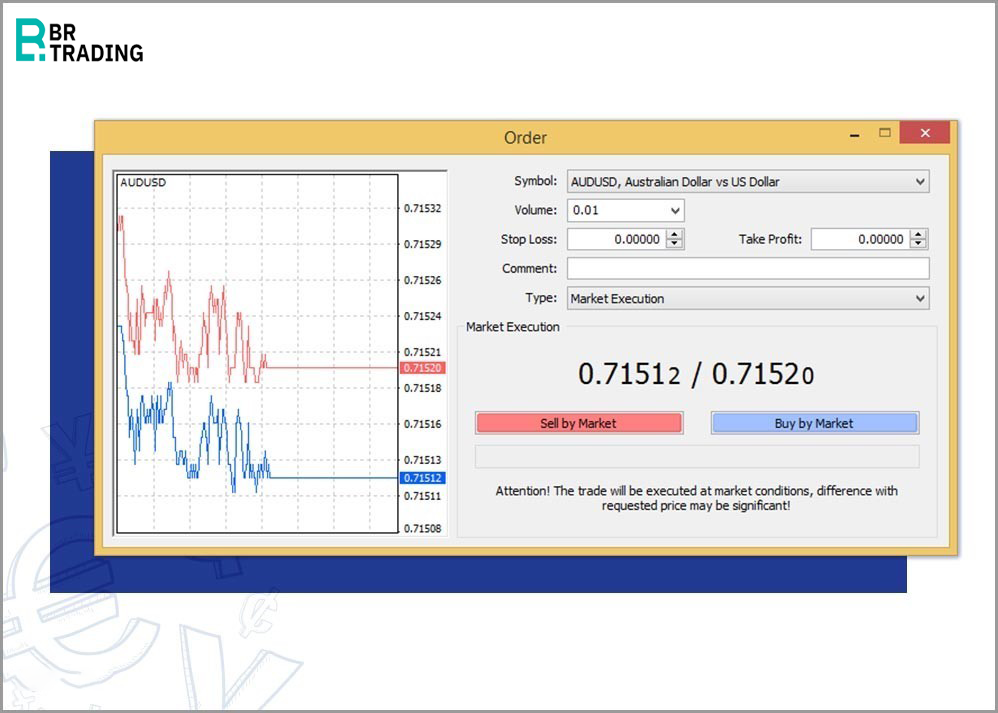
For example, if you open a trade on the AUD/USD pair, the execution box will show two prices: 0.71520 as the ask price (for buying), and 0.71512 as the bid price (for selling). The difference between these two prices represents the spread.
How is the Spread Measured?
The spread is measured in pips. A pip is the smallest price movement in a currency pair and represents the fourth decimal place in the exchange rate, except for currency pairs involving the Japanese yen, where a pip is the second decimal place. The term "PIP" stands for Percentage In Point, which refers to the percentage change represented by a single pip. We've previously explained what a pip is in more detail in another educational article.