- Home
- About us
- Courses
-
News
Others
- ما العملات المستقرة؟ وكيف يجري تنظيمها؟
- المركزي الصيني يواصل شراء الذهب للشهر العاشر على التوالي
- أسبوع حاسم للسياسة النقدية العالمية.. "الفيدرالي" يتأهب لأول خفض للفائدة في عهد ترمب
- الأسواق تترقب خفض الفائدة.. ورهانات صعود الأسهم والسندات تتراجع
- الأسهم الأميركية تبلغ قمة جديدة مع توسع توقعات خفض الفائدة
- بعد خفض الفائدة.. باول يوحد صف الفيدرالي وسط عواصف السياسة والاقتصاد
- آمال الأسواق تتعلق بمكالمة ترمب وشي اليوم.. وهذا كل ما تحتاج لمعرفته
- فقاعة الذكاء الاصطناعي محور نقاشات البنوك المركزية باجتماعات صندوق النقد
- الاقتصاد العالمي على صفيح ساخن بسبب رسوم ترمب والذكاء الاصطناعي والديون
- أميركا تصعّد المواجهة التجارية مع الصين قبيل قمة ترمب وشي
- أسهم آسيا تتراجع و"بتكوين" تهبط دون 86 ألف دولار وسط قلق الأسواق
- مخاوف فقاعة الذكاء الاصطناعي تحكم قبضتها على وول ستريت
- "بتكوين" تفقد ثلث قيمتها من ذروتها التاريخية
-
Education
- Currency Pair System in the Forex Market
- Features and Characteristics of the Forex Market
- The Concept of Leverage and Its Sizes
- The Concept of Financial Markets
- What Is Margin and How Does It Work?
- Types of Forex Market Participants & Their Purposes:
- Swap Benefits or Rollover in Trading
- MetaTrader 4 Program Explanation
- Calculating the Point Value and Profit/Loss Calculation
- Types of Trading Orders in Forex
- Forex Trading Mechanism
- Trading Contracts in the Currency Market
- Understanding Price Movement in the Forex Market
- Understanding Forex Market Sessions and the Power of Liquidity Overlaps
- Top 8 Traded Currencies in the Forex Market and Their Global Impact
- Open Live Account
As we mentioned in previous lessons, one of the advantages of the Forex market is that it operates on an OTC (Over-The-Counter) system. This means it functions 24 continuous hours a day, five days a week, starting Monday through Friday, and closes on Saturday and Sunday as the weekend break.
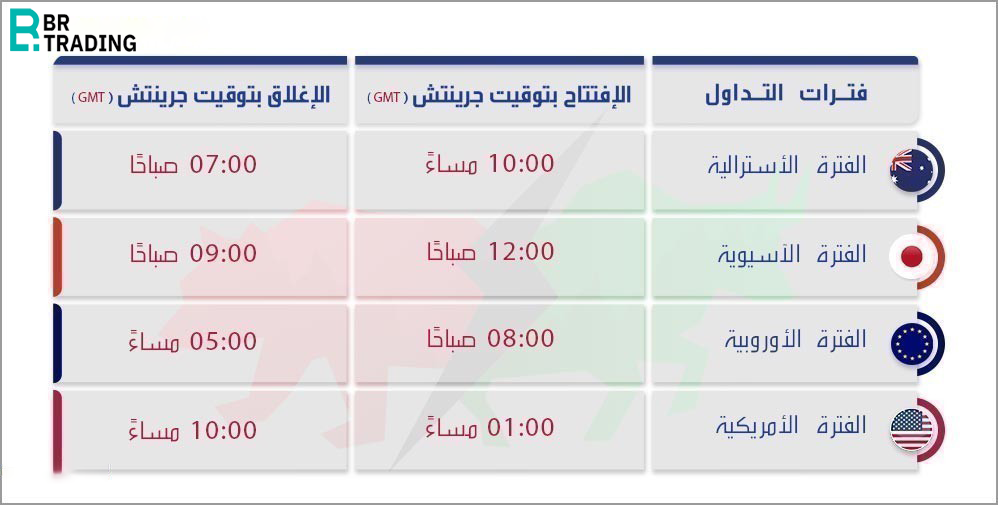
The trading day is divided into several time periods known as market sessions.
The trading begins with the Australian session in Sydney, which runs from 10:00 PM to 7:00 AM GMT.
It overlaps with the Asian session in Tokyo, running from 2:00 AM to 9:00 AM GMT.
Then comes the European session in London, which is considered the most active and liquid session in the Forex market. It runs from 8:00 AM to 5:00 PM GMT.
Finally, there's the American session in New York, which is the second most liquid session, running from 1:00 PM to 10:00 PM GMT.
At the end of the American session, the Australian session begins again, starting a new trading day.
A key highlight is the overlap between the European and American sessions, from 1:00 PM to 4:00 PM GMT, which is the most liquid time in the Forex market due to high trading volume.
Unlike the stock market, Forex doesn't have a centralized trading session with fixed open/close hours where trades can't happen before or after.
In Forex, traders can place and execute trades at any time during the trading week, without being bound by a specific session.
This is possible because Forex trading takes place across different financial centers around the world.
The Forex day begins in New Zealand, followed by Australia (Sydney), then Tokyo (Japan) as part of the Asian session, followed by Hong Kong and Singapore.
After a few hours, trading starts in the Middle East, such as in Bahrain, and then in Europe, with London being the largest financial center not only in Europe but globally.
Finally, the trading day moves to the United States (New York), where the day ends, and then starts again in Sydney.
Forex has no geographical boundaries, and trading is not restricted to any physical location.
It operates through electronic networks under the OTC system, allowing traders to access prices and place trades from anywhere in the world using a trading platform or software.
📘 Stay tuned for the next lesson to learn more about the Forex market.